JK Series
JK Series
The RivetKing JK Series, JK Nut is a low cost alternative to IPB Series in non-load bearing applications. Ideal applications for JK Nuts are when they can be applied to paperboard, cardboard, or thin plastics. For weather resistance, the JK nuts can be coated in vinyl in any color.
- Products
- Product Assistance
- Description
- Design Considerations
- CAD Files
- Catalog
| Part# | Thread Size | Grip Code | Grip Range | Length | Head Diameter | Head Height | Body Diameter | Hole Size | |
| Inch | JK-0401 | 6-32 UNC | #1 | .010 – .060 | .663 | .469 | .073 | .308 | .324 |
| JK-0402 | 6-32 UNC | #2 | .060 – .085 | .900 | .469 | .073 | .308 | .324 | |
| JK-0501 | 10-24 UNC | #1 | .075 – .120 | .703 | .531 | .073 | .378 | .391 | |
| JK-0502 | 10-24 UNC | #2 | .120 – .160 | .875 | .531 | .073 | .378 | .391 | |
| JK-0601 | 1/4-20 UNC | #1 | .010 – .075 | .718 | .625 | .073 | .438 | .444 | |
| JK-0602 | 1/4-20 UNC | #2 | .250 – .350 | .906 | .625 | .073 | .438 | .444 | |
| Metric | JK-0401M | M4 | #1 | 3.81 – 4.75 | 16.84 | 11.91 | 1.85 | 8.08 | 8.23 |
| JK-0402M | M4 | #2 | 4.75 – 9.53 | 22.86 | 12.91 | 1.85 | 8.08 | 8.23 | |
| JK-0501M | M5 | #1 | 3.81 – 4.75 | 17.86 | 13.49 | 1.85 | 9.70 | 9.94 | |
| JK-0502M | M5 | #2 | 4.75 – 9.53 | 22.23 | 13.49 | 1.85 | 9.70 | 9.94 | |
| JK-0601M | M6 | #1 | 3.81 – 4.75 | 18.24 | 15.89 | 1.85 | 11.13 | 11.28 | |
| JK-0602M | M6 | #2 | 4.75 – 9.53 | 23.01 | 15.89 | 1.85 | 11.13 | 11.28 |
Industrial Rivet & Fastener Co. can help you select the right product or tool for your application. Please contact our experienced Product Specialists with any questions. We look forward to hearing from you! 1-800-BUY-RIVET or info@rivet.com
Type: JK Series Rivet Nut
Material: Steel
Finish: Zinc Cr3, ROHS Compliant
Design Considerations
Grip Range:
Determining the length of the rivet nut is critical to ensure the rivet will function as intended. If the rivet nut is applied over or under its intended grip range, it may not work properly. All manufacturers list a range of material thickness in which the product will perform properly. This thickness is commonly called the grip range. Setting rivet nuts outside of their specified grip range can lead to functional failures.
Also be sure to account for the theoretical grip versus the actual grip. While the grip may be calculated by adding the thickness of the two materials together, be sure to account for any burrs, bends and manufacturing tolerances which may increase or decrease the overall grip of the materials being riveted.
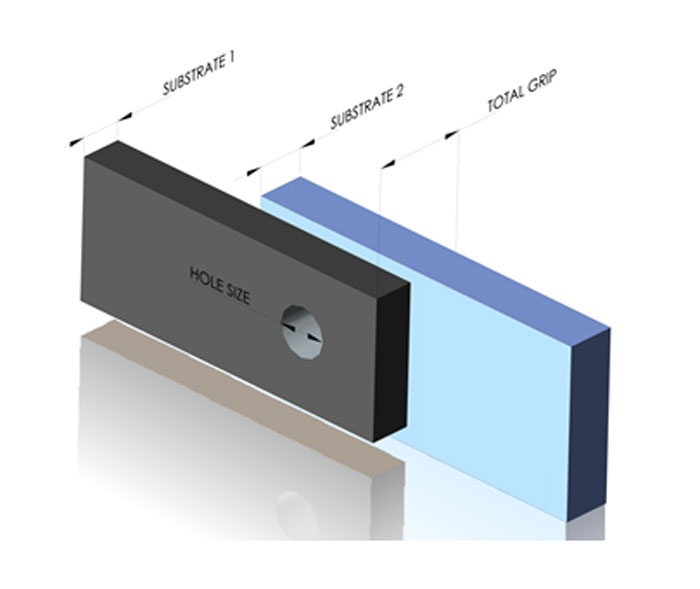
Hole Size:
Hole sizes are extremely important for the proper functionality of rivet nuts. We specify a hole size for every rivet we manufacture. A rivet nut is only guaranteed to function as designed when the hole size is within the prescribed range. Additionally, the design engineer should calculate the manufacturing tolerances of the hole to ensure proper fit so that interference issues will not occur later.
Joint Materials & Strength:
It is sometimes necessary to use dissimilar materials such as fastening aluminum to steel or plastics to aluminum. Whenever possible, the stronger material should be the secondary side because this is where the setting will take place. As a general rule, a rivet nut should be used in materials equal to or greater than its own strength, although there are rivet nuts designed to work in softer materials. Be sure to verify the compatibility of the rivet materials as galvanic corrosion can occur and is seldom considered in the design phase.
Tool Clearance:
Sufficient clearances are needed so that the tool can access the joint being riveted without interference. Be sure to account for the riveting equipment in the design phase to prevent the need for customized and potentially costly tooling modifications.
Head Clearance:
Axial access is required on the primary side being riveted to allow for the flange to overlap the hole without interference. When designing the primary hole, be sure to calculate the head diameter and its tolerances as well as the layout footprint of the head around the hole. This is especially critical when riveting hardware next to bends, folds, extrusions and/or cutouts on the applications.
Blind Side Clearance:
Since the blind side of the rivet nut is designed to form into a secondary flange, it is important to leave room for the flange to expand and seat properly. Keep in mind, the collapsed height is shorter than the pre-installed height. Therefore, be sure the secondary side can accommodate the entire rivet nut length, before riveting. Testing should be done in the design phase to calculate what distances are needed and to verify proper functionality.
Corrosion Protection:
The corrosion factor of a particular rivet nut is dependent on the corrosivities of the base metal, the protective layer (plating) and the conversion layer (chromate). Being that the most cost effective material to manufacture is steel, most prefer to protect the steel with a plating such as Zinc Chromate, or other alloy platings. For standard performance, an SST rating of 24 hours until red rust is common. Other platings such as zinc alloys (Zinc Nickel, Zinc Iron, Tin Zinc) are available which can extend the SST rating to 840 hours until red rust. All specified finishes are tested by RivetKing in accordance with ASTM B117 standards.
CAD Files
The following are available for download upon request by emailing engineering@rivet.com:
.dxf
.dwg
.IGES
.SLDPRT